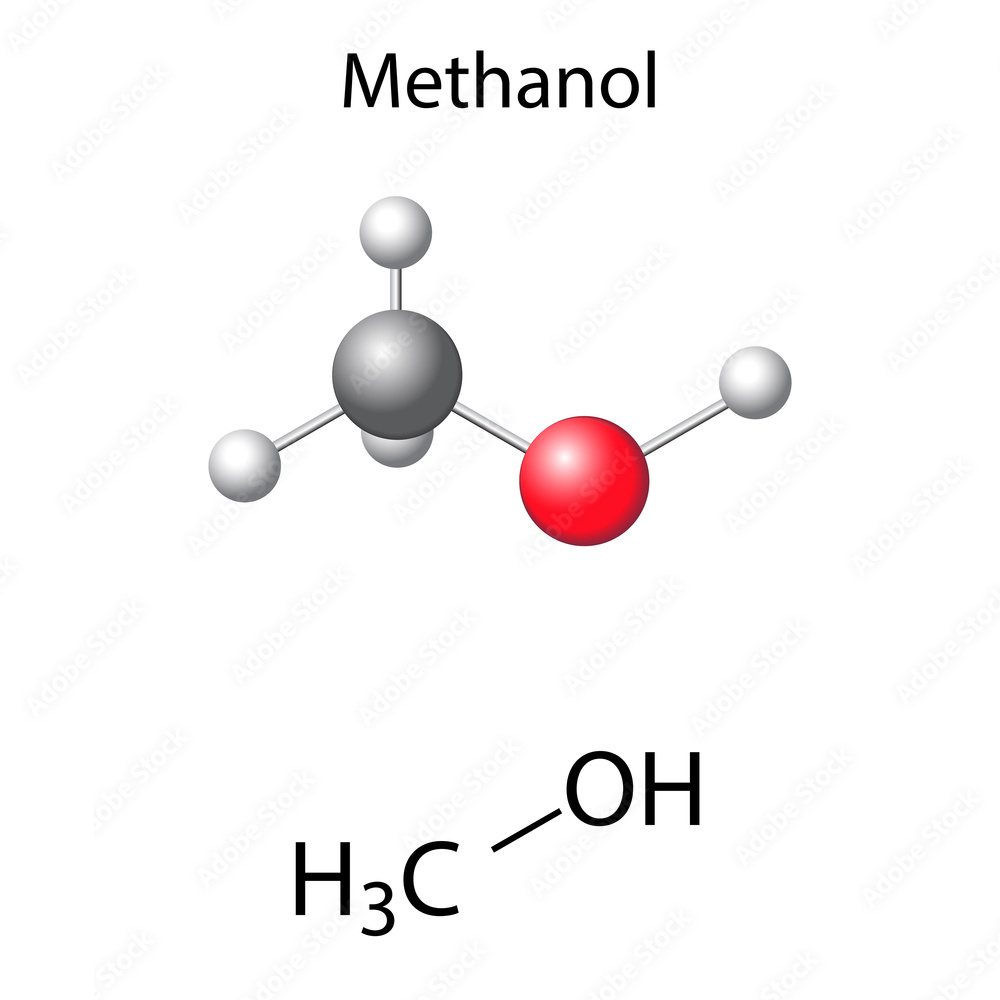
It is the simplest of alcohols. It comes in the form of a light, volatile, colorless, flammable, toxic liquid with a characteristic odor, softer and sweeter than that of ethanol
It is called “wood alcohol” because it was once a by-product of wood distillation. Growing plants produce small amounts of methanol, which vary by plant, season, and growing conditions.
Methanol occurs naturally in animal organisms (including humans), in plants and therefore in food.
It is also produced by fermentation and degradation of organic compounds (leaf) as well as through animal metabolisms.
The main source of methanol for humans is their diet, when consuming fresh fruits and vegetables, fruit juices, fermented beverages and low-fat foods containing aspartame.
Methanol, Chemical and physical properties
Appearance and odor: Clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic pungent odor, transparent liquid without non-soluble impurities
| Molecular weight (gr/mol); | 32.05 |
| Boiling point (degrees Fahrenheit): | 148 |
| Melting point (degrees Fahrenheit): | -144 |
| Vapor pressure (mm of mercury): | 97@68°F |
| Specific gravity (water = 1): | 0.791 |
| Density under 20°C, g/cm3: | 0.791-0.792 |
| Vapor density (air = 1): | 1.1 |
| Percent volatile (by weight): | 99.9 |
| Acidity (%): | <0.03 |
| Solubility in water: | Totally miscible |
| Evaporation rate (butyl acetate = 1): | 5.9 |
| Ethanol (ppm): | <2.0 |
| Iron + Sodium + Cupper (ppm): | <0,5 |
| Water content, %not more than: | 0-05 |
| Purity % WT on dry basis, min: | 99.85 |